10 REASONS OF YOUR ITCHY SKIN
1. Dry skin is a common cause of itching
Dry skin often serves as a primary culprit behind the uncomfortable sensation of itching. When the skin lacks proper hydration, it can become parched and rough, leading to irritation and the urge to scratch.
Various factors, including weather conditions, harsh soaps or skincare products, and underlying skin conditions like eczema or psoriasis, can contribute to the development of dry skin. As the skin’s protective barrier becomes compromised, moisture loss occurs more readily, exacerbating the dryness and triggering itching sensations.
Additionally, aging and certain medical conditions or medications can further compromise the skin’s ability to retain moisture, leading to increased susceptibility to dryness and itching. To address itching caused by dry skin, it’s essential to prioritize hydration and adopt a skincare routine that focuses on replenishing moisture and restoring the skin’s barrier function.
Read Also:
Tips for a Good Night’s Sleep: Creating a Relaxing Bedtime Routine
2. Allergies trigger itching
Itching can often be triggered by allergies, as the body’s immune system reacts to allergens in the environment. Allergies occur when the immune system mistakenly identifies harmless substances, such as pollen, pet dander, or certain foods, as threats.
In response to exposure to these allergens, the immune system releases histamine and other chemicals, which can cause inflammation and irritation in the skin, leading to itching.
Common allergic reactions that manifest as itching include allergic rhinitis (hay fever), allergic dermatitis (eczema), and allergic conjunctivitis (eye allergies). Itching associated with allergies may vary in intensity and location, depending on the specific allergen and individual sensitivity. In addition to skin itching, allergy symptoms may also include sneezing, nasal congestion, watery eyes, and throat irritation.
3. Eczema can be the reason behind your itchy skin
Eczema, also known as atopic dermatitis, is a chronic skin condition characterized by inflammation, redness, and itching. Itching is a hallmark symptom of eczema and can range from mild to severe, causing significant discomfort and disruption to daily life.
Eczema occurs when the skin’s natural barrier becomes compromised, leading to increased moisture loss and susceptibility to irritants and allergens.
This can trigger an inflammatory response in the skin, resulting in itching and the development of characteristic eczematous lesions. Itching associated with eczema tends to be persistent and may worsen at night, leading to sleep disturbances and further exacerbating the condition. Common triggers for eczema itching include dry skin, exposure to irritants such as harsh soaps or detergents, allergens such as pollen or pet dander, and emotional stress.
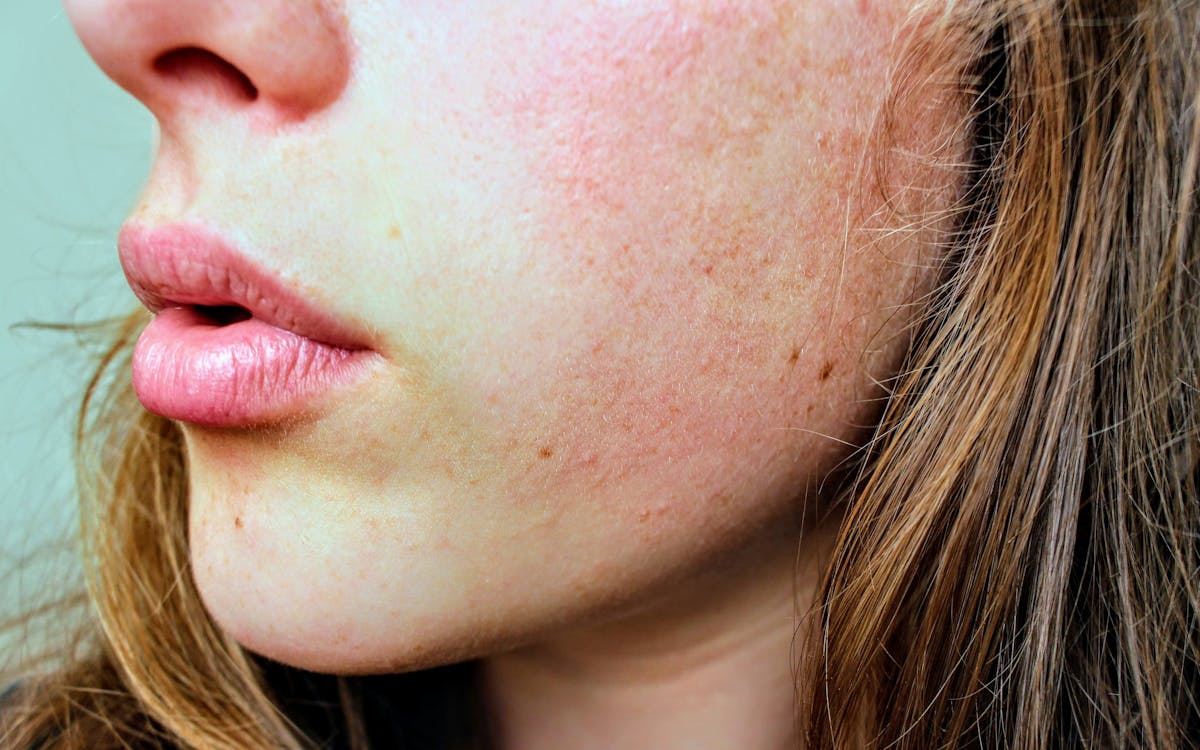
4. Psoriasis can make skin itchy
Psoriasis is a chronic autoimmune condition characterized by the rapid buildup of skin cells, leading to the development of thick, scaly patches on the skin’s surface. Itching, or pruritus, is a common symptom of psoriasis and can range from mild to severe, causing significant discomfort and distress for affected individuals.
Itching in psoriasis is often exacerbated by factors such as dryness, inflammation, and the presence of psoriatic plaques, which can become cracked and fissured, further contributing to the sensation of itching.
Additionally, itching associated with psoriasis may be triggered or worsened by environmental factors, stress, and certain medications. Managing psoriasis-related itching involves a comprehensive approach that addresses both the underlying inflammation and the symptoms of dryness and irritation.
5. Insect Bites cause itching of skin
Insect bites are a common cause of itching of the skin, often resulting from the injection of saliva or venom by biting insects such as mosquitoes, fleas, bedbugs, or ants.
The saliva or venom contains proteins and other substances that can trigger an immune response in the skin, leading to inflammation and itching. The severity of itching associated with insect bites can vary depending on factors such as the type of insect, the individual’s sensitivity to insect bites, and the location of the bite.
Itching from insect bites is typically accompanied by redness, swelling, and sometimes pain or discomfort at the site of the bite. Scratching insect bites can further irritate the skin and increase the risk of infection, so it’s important to resist the urge to scratch and instead apply topical anti-itch creams or lotions to help alleviate itching and reduce inflammation.
6. Contact Dermatitis can cause itchy skin
Contact dermatitis is a type of skin inflammation that occurs when the skin comes into contact with irritating substances or allergens. Itchy skin is one of the hallmark symptoms of contact dermatitis, along with redness, swelling, and sometimes the development of blisters or rash.
Contact dermatitis can be caused by a wide range of substances, including soaps, cosmetics, jewelry, latex, and certain plants such as poison ivy or poison oak.
When the skin is exposed to these irritants or allergens, it triggers an immune response that leads to inflammation and itching. The severity of itching associated with contact dermatitis can vary depending on the individual’s sensitivity to the offending substance and the duration of exposure.

7. Skin Infections cause itching
Itching is a common symptom associated with various types of skin infections, ranging from fungal infections like ringworm or athlete’s foot to bacterial infections such as impetigo or cellulitis. Skin infections can occur when microorganisms such as bacteria, fungi, or viruses invade the skin, leading to inflammation and irritation.
Itching is often a result of the body’s immune response to the infection, as inflammatory chemicals are released to combat the invading pathogens. Additionally, the presence of infection can disrupt the skin’s natural barrier function, making it more susceptible to dryness and irritation, which can further exacerbate itching.
The severity of itching associated with skin infections can vary depending on the type and extent of the infection, as well as individual factors such as skin sensitivity and immune function.
Read Also:
How To Reduce Your Weight Under 45 Days: Tips And Solutions
8. Hives caused by allergic reactions can cause itchiness
When it comes to allergic reactions, hives are a common manifestation that often brings along intense itchiness. Hives, also known as urticaria, are raised, red welts on the skin that can vary in size and shape.
They occur as a result of the body’s immune response to allergens, such as certain foods, medications, insect stings, or environmental triggers like pollen or pet dander. The release of histamine and other inflammatory chemicals in response to allergen exposure leads to the characteristic appearance of hives and the accompanying sensation of itchiness.
This itching can be extremely bothersome and disruptive, often leading to scratching that can further irritate the skin and exacerbate the hives. Managing the itchiness associated with hives involves identifying and avoiding triggers whenever possible and using antihistamines or other medications to alleviate symptoms.
9. Menopause can lead to itchy skin
Menopause is a significant transitional phase in a woman’s life, marked by hormonal changes that can impact various aspects of health, including the skin. Itchy skin, also known as pruritus, is a common symptom experienced by many women during menopause. The hormonal fluctuations that occur during menopause, particularly the decrease in estrogen levels, can lead to changes in the skin’s structure and function.
These changes can result in decreased moisture levels, reduced elasticity, and thinner skin, all of which can contribute to itching and discomfort. Additionally, menopausal symptoms such as hot flashes and night sweats can exacerbate itching by causing further dryness and irritation of the skin.
Managing itchy skin during menopause involves adopting a comprehensive approach that addresses both the underlying hormonal changes and the symptoms of dryness and irritation. This may include using moisturizers and emollients to hydrate the skin, avoiding harsh soaps and skincare products, and maintaining a healthy lifestyle that includes a balanced diet and regular exercise.

10. Some medications can cause itching effects
Itching, also known as pruritus, can be a side effect of certain medications, ranging from prescription drugs to over-the-counter remedies.
Medications that commonly cause itching include antibiotics, pain relievers, antifungal medications, and certain blood pressure or cholesterol-lowering drugs. The itching may occur as a result of an allergic reaction to the medication or as a direct effect of the drug on the skin.
Additionally, medications can sometimes disrupt the body’s natural balance, leading to dryness or irritation of the skin, which can contribute to itching. It’s important to note that itching caused by medications can vary in severity and may occur alone or with other symptoms such as rash, hives, or swelling. Managing itching caused by medications involves identifying the offending drug and discontinuing its use if possible.