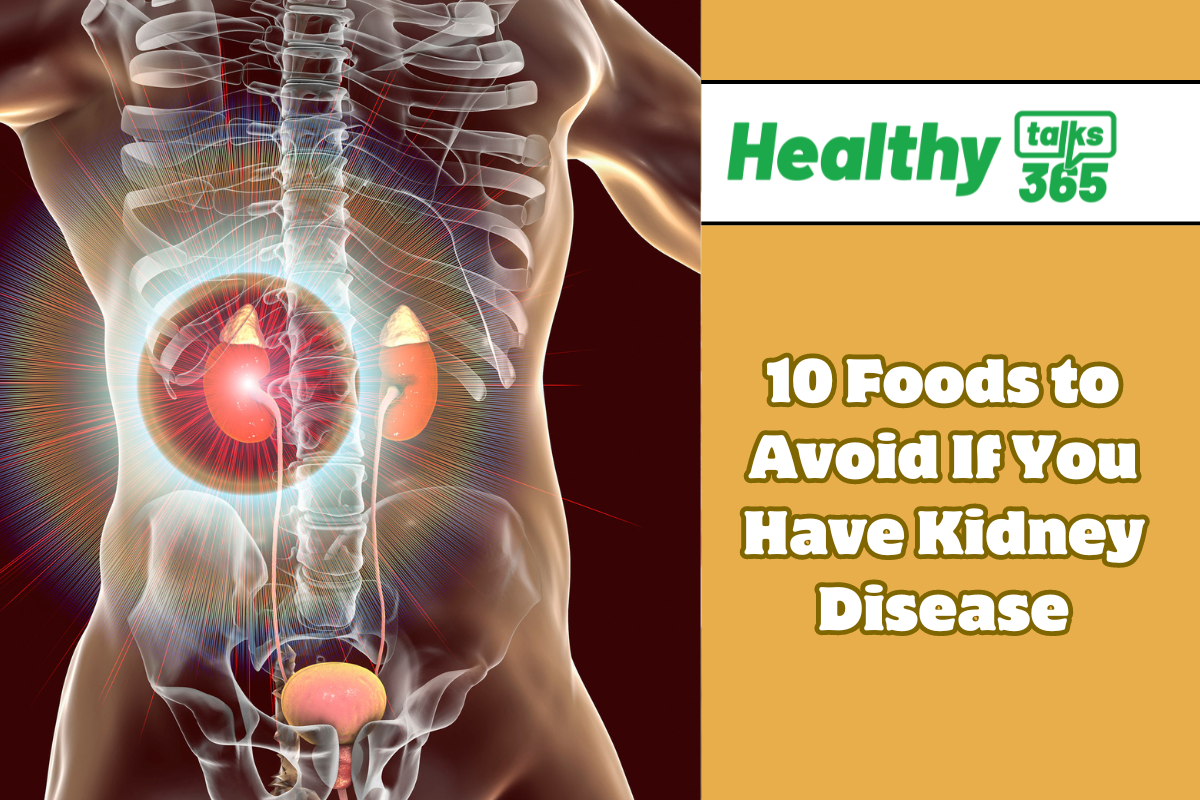
10 Foods to Avoid If You Have Kidney Disease
1. Avoid high sodium foods if you have kidney disease
For individuals with kidney disease, limiting the intake of high-sodium foods is crucial for managing their condition and supporting kidney health. High levels of sodium can contribute to fluid retention and increased blood pressure, both of which can further strain the kidneys and worsen kidney function.
By avoiding high-sodium foods such as processed meats, canned soups, salty snacks, and fast food, individuals with kidney disease can help reduce their risk of complications and slow the progression of the disease. Instead, opting for fresh, whole foods and cooking at home allows for better control over sodium intake and promotes a kidney-friendly diet.

2. Processed foods can be harmful for kidney patients
Processed foods pose a significant risk to individuals with kidney disease due to their high levels of sodium, phosphorus, and other additives that can exacerbate kidney-related complications. These foods often contain preservatives, flavor enhancers, and other additives that can be harmful to kidney health.
Avoiding processed foods is essential for managing kidney disease and minimizing the risk of further damage to the kidneys. Instead, focusing on whole, unprocessed foods such as fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins allows individuals with kidney disease to control their intake of harmful substances and support overall kidney function.
Read Also:
Pregnancy: Signs, Symptoms, Overview, Health Tips You Should Know
3. High potassium foods can be dangerous if you have kidney disease
For individuals with kidney disease, consuming foods high in potassium can pose serious health risks. High levels of potassium in the blood, known as hyperkalemia, can occur when the kidneys are unable to properly filter and excrete excess potassium from the body.
Avoiding high-potassium foods is essential for managing kidney disease and preventing complications associated with hyperkalemia. These foods include bananas, oranges, potatoes, tomatoes, and leafy greens, among others. By limiting the intake of these foods, individuals with kidney disease can help maintain safe potassium levels in the blood and reduce the risk of adverse health effects.

4. Avoid high phosphorus food if you have kidney disease
Individuals with kidney disease should steer clear of foods high in phosphorus, as excessive phosphorus intake can lead to complications such as mineral imbalances, bone disease, and cardiovascular issues. High phosphorus levels in the blood, known as hyperphosphatemia, can occur when the kidneys are unable to properly regulate phosphorus levels in the body.
Individuals with kidney disease should be mindful of food additives and preservatives that may contain phosphorus. Reading food labels carefully and choosing low-phosphorus or phosphorus-free alternatives can help reduce phosphorus intake and support kidney health.
5. Foods high in added sugars are harmful if you have kidney disease
Avoiding foods high in added sugars is essential for managing kidney disease and reducing the risk of complications associated with diabetes and obesity. These foods include sugary beverages, processed snacks, desserts, and sweetened cereals, among others. By limiting the intake of these foods, individuals with kidney disease can help control their blood sugar levels and reduce the risk of kidney-related complications.
In addition to avoiding foods high in added sugars, individuals with kidney disease should focus on consuming whole, unprocessed foods that are naturally low in sugar. This includes fruits, vegetables, whole grains, lean proteins, and healthy fats. These foods provide essential nutrients and fiber without the added sugars that can contribute to health problems.
Read Also:
6. High protein foods should be avoided by kidney patients
Excessive protein intake can lead to the accumulation of waste products in the blood, such as urea and creatinine, which can be harmful to kidney function. By limiting their protein intake, individuals with kidney disease can help minimize the buildup of these waste products and reduce the risk of complications.
However, it’s important for kidney patients to ensure they are still getting adequate nutrition despite reducing their protein intake. Working with a healthcare provider or registered dietitian can help individuals with kidney disease develop a balanced diet plan that meets their nutritional needs while also supporting kidney health.

7. Dark coloured sodas are harmful for kidney health
Dark-colored sodas, such as cola drinks, pose significant risks to kidney health due to their high content of phosphoric acid and added sugars. These beverages have been linked to various kidney-related issues, including kidney stones, decreased kidney function, and an increased risk of chronic kidney disease.
The phosphoric acid found in dark-colored sodas can contribute to the formation of kidney stones by binding with calcium in the urine, leading to the formation of insoluble crystals. Additionally, excessive consumption of phosphoric acid can impair kidney function and increase the risk of kidney damage over time.
8. Avoid alcohol consumption in case of kidney disease
In cases of kidney disease, abstaining from alcohol consumption is highly recommended to prevent exacerbating the condition and safeguard overall kidney health. Alcohol can have detrimental effects on the kidneys, particularly in individuals with compromised kidney function, as it can disrupt the body’s fluid balance, increase blood pressure, and impair kidney function.
Alcohol consumption can lead to dehydration, which can strain the kidneys and hinder their ability to effectively filter waste products from the blood. Chronic dehydration can also contribute to the formation of kidney stones and increase the risk of kidney damage over time.
9. Caffeine intake can adversely affect kidney health of kidney patients
Caffeine intake can have negative implications for the kidney health of individuals with kidney disease. The stimulant properties of caffeine can lead to increased blood pressure and heart rate, which may put additional strain on the kidneys. Moreover, caffeine is known to have diuretic effects, meaning it can increase urine production and potentially lead to dehydration. Dehydration can impair kidney function and exacerbate symptoms associated with kidney disease.
Furthermore, excessive caffeine consumption has been linked to an increased risk of kidney stone formation. Caffeine can increase the concentration of calcium in the urine, which may contribute to the development of calcium-based kidney stones. Additionally, caffeine can interfere with the body’s absorption of calcium and other minerals, further impacting kidney health.

10. Consume whole wheat bread if you have kidney disease
Opting for whole wheat bread can be a beneficial choice for individuals managing kidney disease. Whole wheat bread is a nutritious option that provides essential nutrients such as fiber, vitamins, and minerals, which are important for overall health and well-being. Additionally, whole wheat bread has a lower glycemic index compared to refined white bread, meaning it can help regulate blood sugar levels and promote better blood glucose control, which is important for individuals with kidney disease, particularly those with diabetes.
Whole wheat bread is a versatile food that can be enjoyed in a variety of ways, from sandwiches and toast to bread pudding and croutons. It can be easily incorporated into a kidney-friendly diet that emphasizes whole, nutrient-rich foods and limits processed and refined products.